Anti-Claudin-2 Antibody for IBD Therapy
January 4, 2021
Anti-claudin-2 antibody improves IBD intestinal barrier destruction by claudin-2
Background / Context / Abstract:
The epithelial tight junction controls the paracellular transport in the intestine and also prevents uptake of larger molecules. Claudin-2, one of the claudin-family regulating intercellular tight junction, forms a paracellular channel for small cations and water. It is expressed in leaky epithelia in small intestine for the paracellular transport of sodium, potassium, and fluid. In inflammatory bowel diseases, claudin-2 is upregulated in small and large intestine and leads destruction of intestinal barrier and diarrhea via a leak flux mechanism.
Technology Overview:
Here, we developed a new anti-claudin-2 mAb binding to extracellular domain of claudin-2. It suppressed claudin-2 function on paracellular transport and improved barrier function of bowel in IBD model.
Benefits:
・Claudin-2 is a new therapeutic target of IBD.
・The antibody binds to extracellular domain of claudin-2 and improves barrier function of bowel.
State of Development / Opportunity / Seeking:
●Opportunity
・Available for exclusive and non-exclusive licensing
・Exclusive/non-exclusive evaluation for defined period (set up for options)
・Collaborative/supportive research
●Seeking
・Licensing
・Development partner
IP Status:
WO2018/123949 (PCT applied in Japanese)
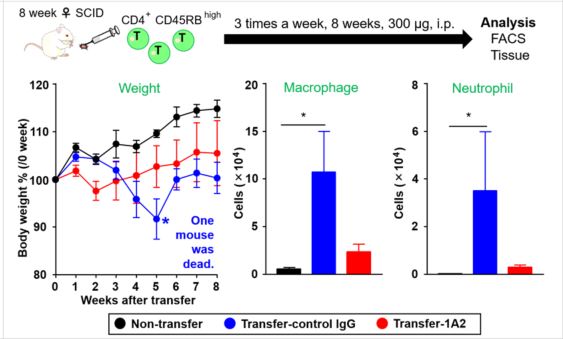
Figures:
In vivo test with T-cell transferred intestine inflammation model micerevealed the anti-clanduin-2 mAb 1A2 suppressed some factors regarding toinflammation and showed improvement of intestine tissue.
Contact:
![]()